Project
Research Projects
- Using Multi-modal Transportation Data For Energy Prediction and Management in Buildings (2019)
Motivation: Urban systems, including transporations and buildings are highly interrelated given the spatial-temporal flow of system users. The change of magnitude of occupancy in one system can be in proportion to the fluctuation in one another. In this project we aim at investigating the edge potential of predicting the energy profile of buildings, from the rich and fine-grained transportation data including realtime traffic flow intensity, and public transit status. The refined prediction would further improve the performance of Model Predictive Control (MPC) on building energy management. link.
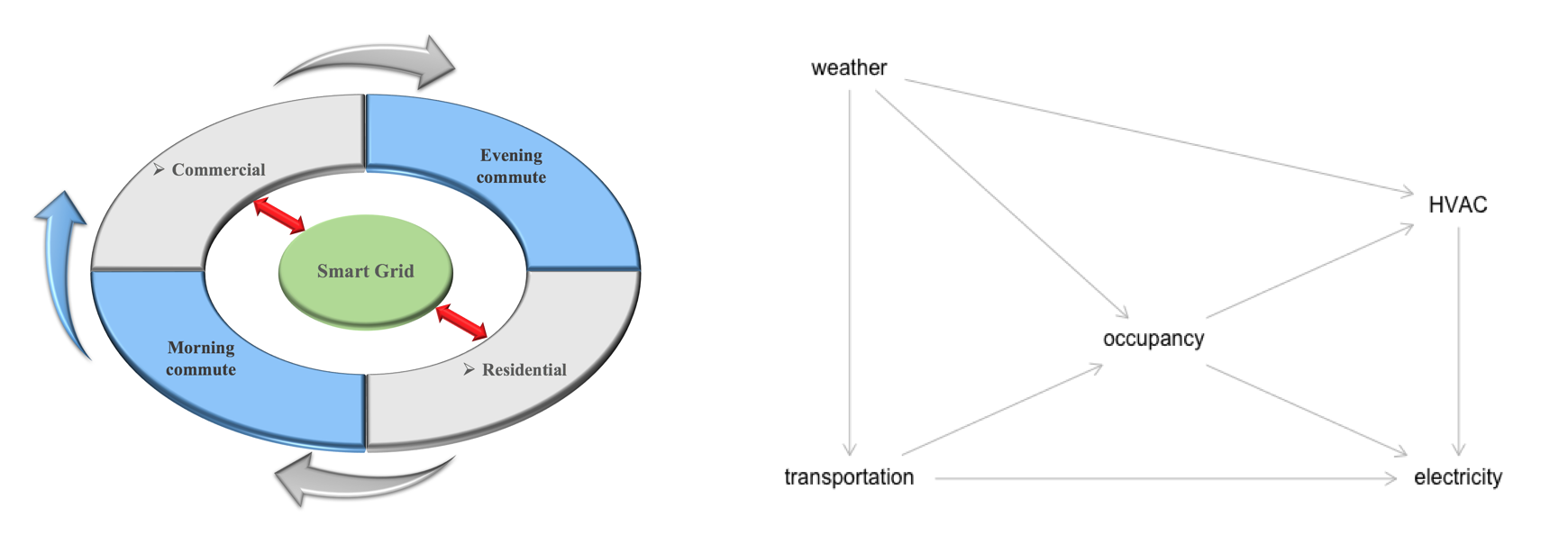
Modeling: The problem is formulated as a m-to-n task, i.e., to prediction the energy profile at next n quarters using all information available up to m quarters ago. A Spatial-Temporal Graph Attention Network (STGAT) framework is proposed to capture the heterogeneous dynamic of public transit (bus) and traffic flow (inrix), where the integrated information is passed to fully-connected networks with historical energy profile and weather features to make the prediction. When compared with state-of-the-art time series baseline models, it is validated the inclusion of ambient transporation reduced the overall RMSE from 0.0478 to 0.0418.
- Enhancing Vision-based Vehicle Detection and Tracking with Transportation Domain Features (2019)
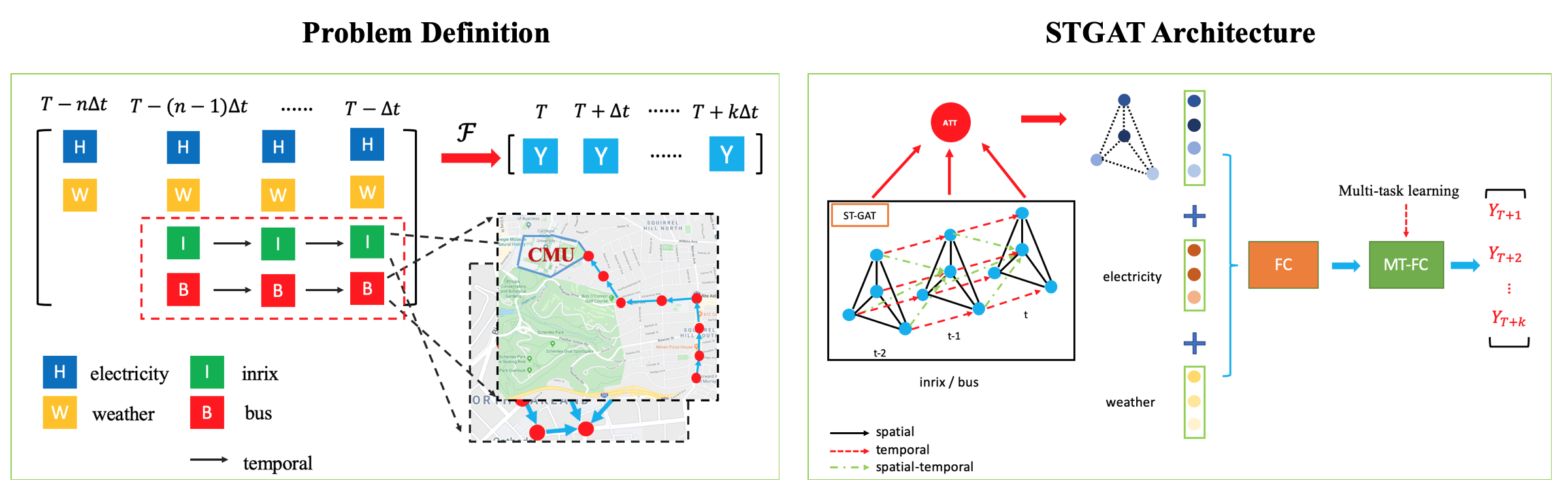
Motivation: Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) are critical components to strengthen travel safety, reduce congestion and improve urban mobilities. The reliability of the system depends on spatial-temporal analytics of key traffic parameters such as density, volume, and speed, which are inferred from sensors including loop detectors and cameras using computer vision. However, the former sensors suffer from high initial costs and low frequency, while the latter may deteriorate in high occlusion and large perspective cases. Thus, in this series of research we explore the effectiveness of fusing features captured by existing transportation sensors and vision-based models for traffic parameter inference. Specifically, we have leveraged domain features with convolutional neural networks to estimate vehicle density and speed (through tracking) separately. Compared with pure visual techniques, it is validated that the inclusion of domain features improves the overall performance, and we look forward to expanding the model for other transportation tasks in future.
Detection: To esimate the density of vehicles, we implemented a model with CNN+rLSTM module for image inputs, and LSTM module for processed transportation features including location of buses and average traffic speed. Compared with pure vision-based detection model YOLO, we have reduced the MAE from 0.73 to 0.27, and justified the effectiveness of domain features. The detailed implementation can be found here.
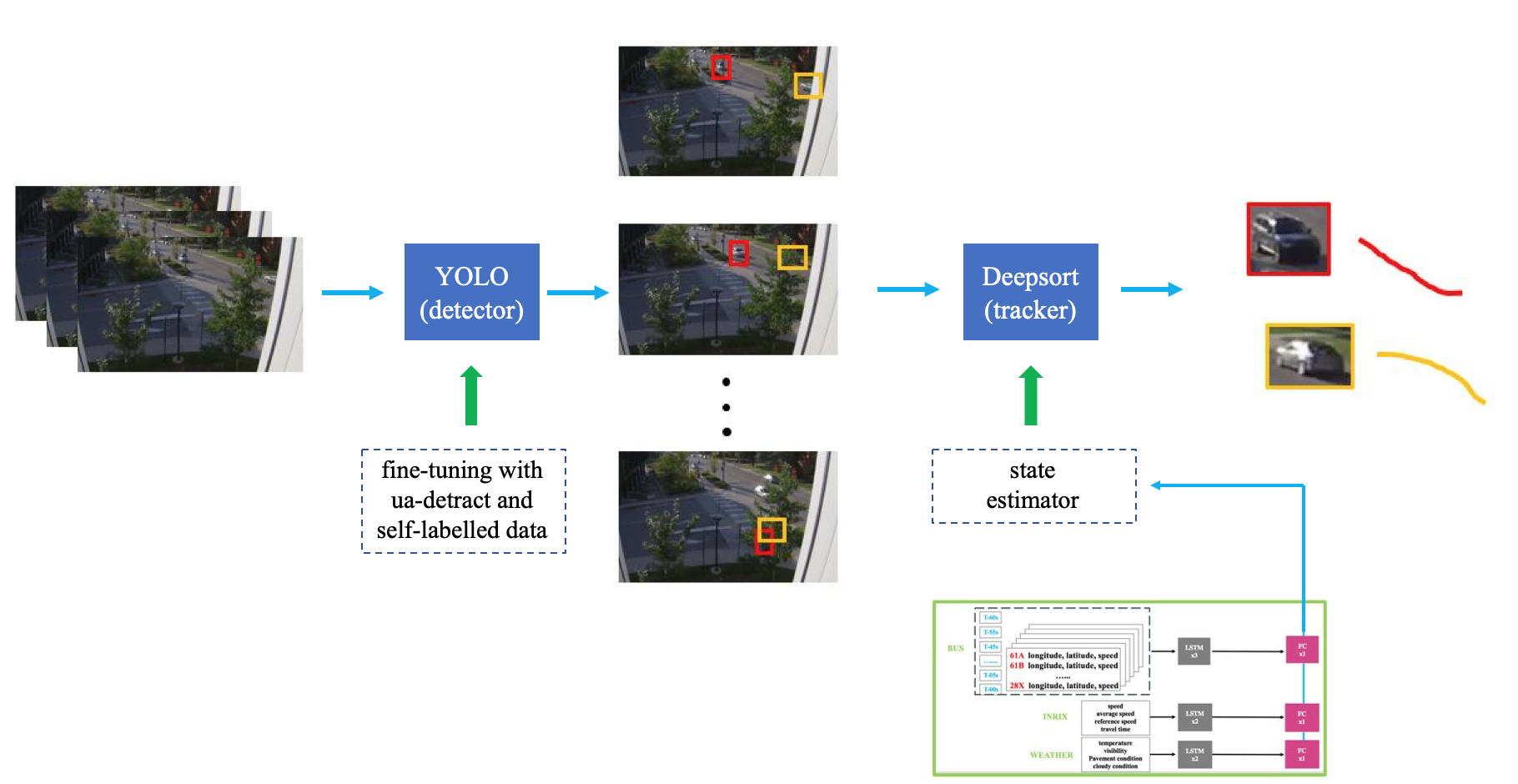
Tracking: The speed estimation problem is tackled by tracking-by-detection framework. Basically, we have fine-tuned YOLO with self-labelled data as detector, and adopted Deepsort framework as tracker. However, we used LSTM network trained with transportation features instead of the Kalman filter as the state estimation module. In addition, the deep appearance descriptor was fine-tuned using UA-DETRAC and self-labelled data. Tested on one hour’s data, it is validated that the fused model improved MOTP from 78.5% to 80.6%, and MOTA from 65.7% to 68.3% respectively. A sample result is attached below.
Course Projects
- Object Counting by Leveraging CNN and LSTM with Multi-Source of Input (2017)
- Designed and implemented a framework by leveraging CNN, LSTM and residual layer for vehicle counting, given input images suffering from low framerate, low resolution, high occlusion and large perspectives.
- Trained and validated the model on TRANSCOS dataset with ~1200 images, evaluated the effectiveness of various data augmentation tricks such as flipping, cropping, and adjusting contrast/brightness.
- Attained a 4.47 MAE that is comparable to state-of-the-art models. The full report can be found here.
- Regression Analysis (2019)
- Investigated patterns and developed classification models that help to refine advertising strategies for regular check-ups in less developed countries. The full report is listed here. Essentially,
- A random forest model is chosen to rank the importance of covariates that motivate regular check-ups.
- A logistic regression model is implemented to identify key features and reference likelihood of the people that can be potentially persuaded for check-up.
- Investigated patterns and developed classification models that help to refine advertising strategies for regular check-ups in less developed countries. The full report is listed here. Essentially,
- Reinforcement Learning (2017)
